6. Cognition (Ch 7)
6.1 Intelligence and Creativity
- Intelligence is our inherent potential for learning
- How well you solve problems
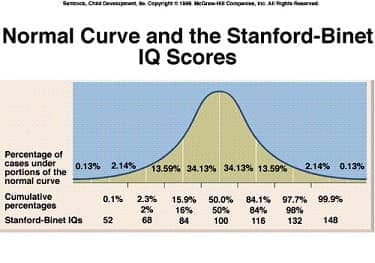
- Alfred Binet
- first intelligence test
- intelligence quotient (IQ)
- comparison between test taker score and average

- g-factor theory of intelligence(Charles Spearman)

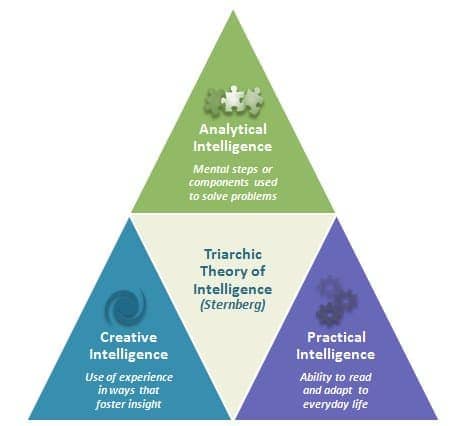
- Triarchic theory of intelligence (Robert Sternberg)
- analytic intelligence (academic skills)
- practical intelligence (problem solving)
- creative intelligence
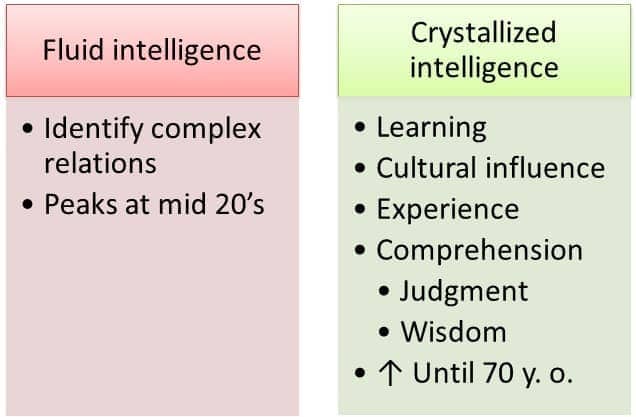
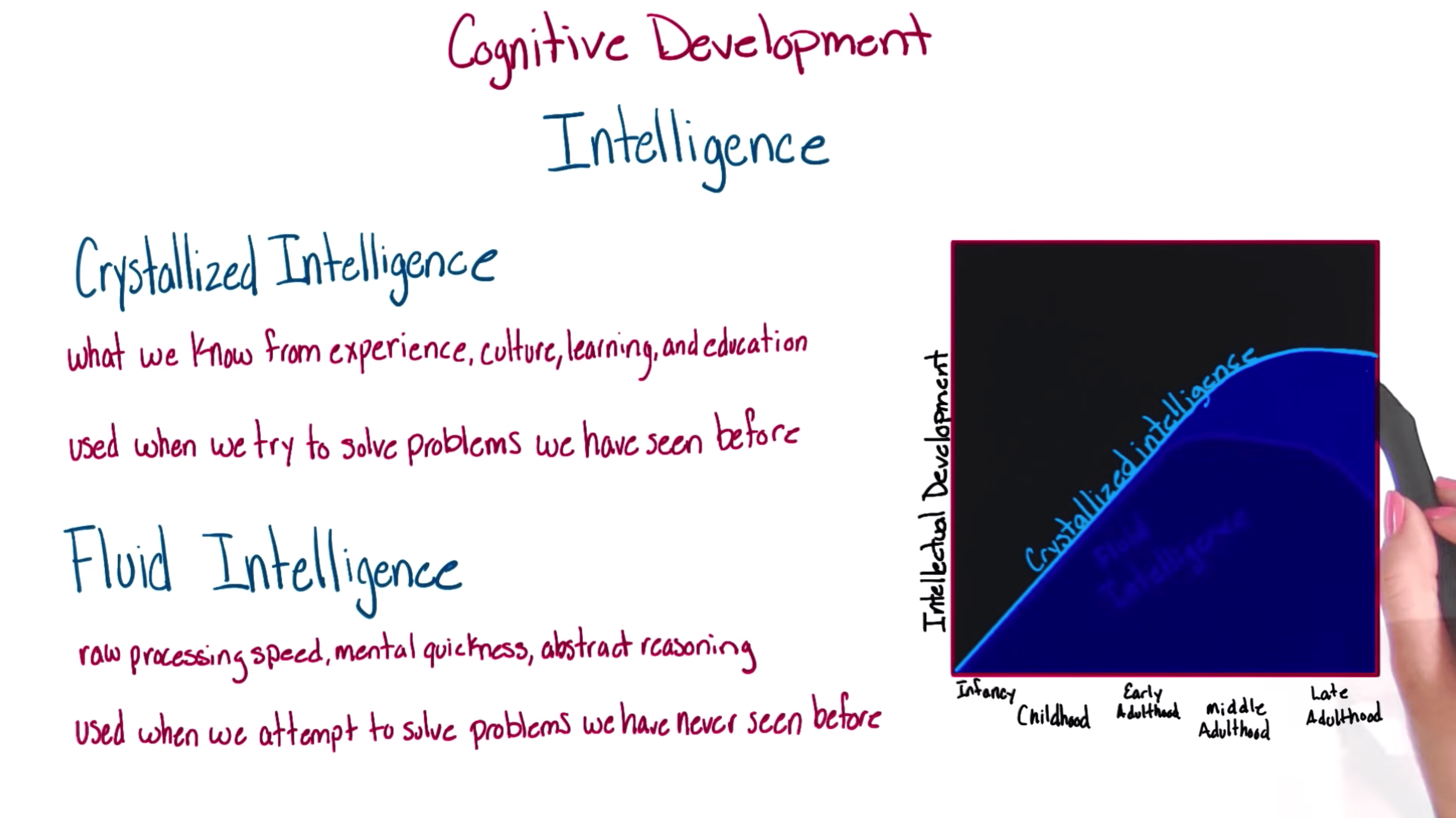
- Fluid intelligence (Raymond Cattell)
- How fast you can learn new things
- respond to your environment
- puzzle ability
- Crystallized intelligence (Raymond Cattell)
- Using skills, experience and learned knowledge to solve problems
- What leads to differing levels of intelligence?
- Nature vs nurture
- intelligence hereditary
- learning environment
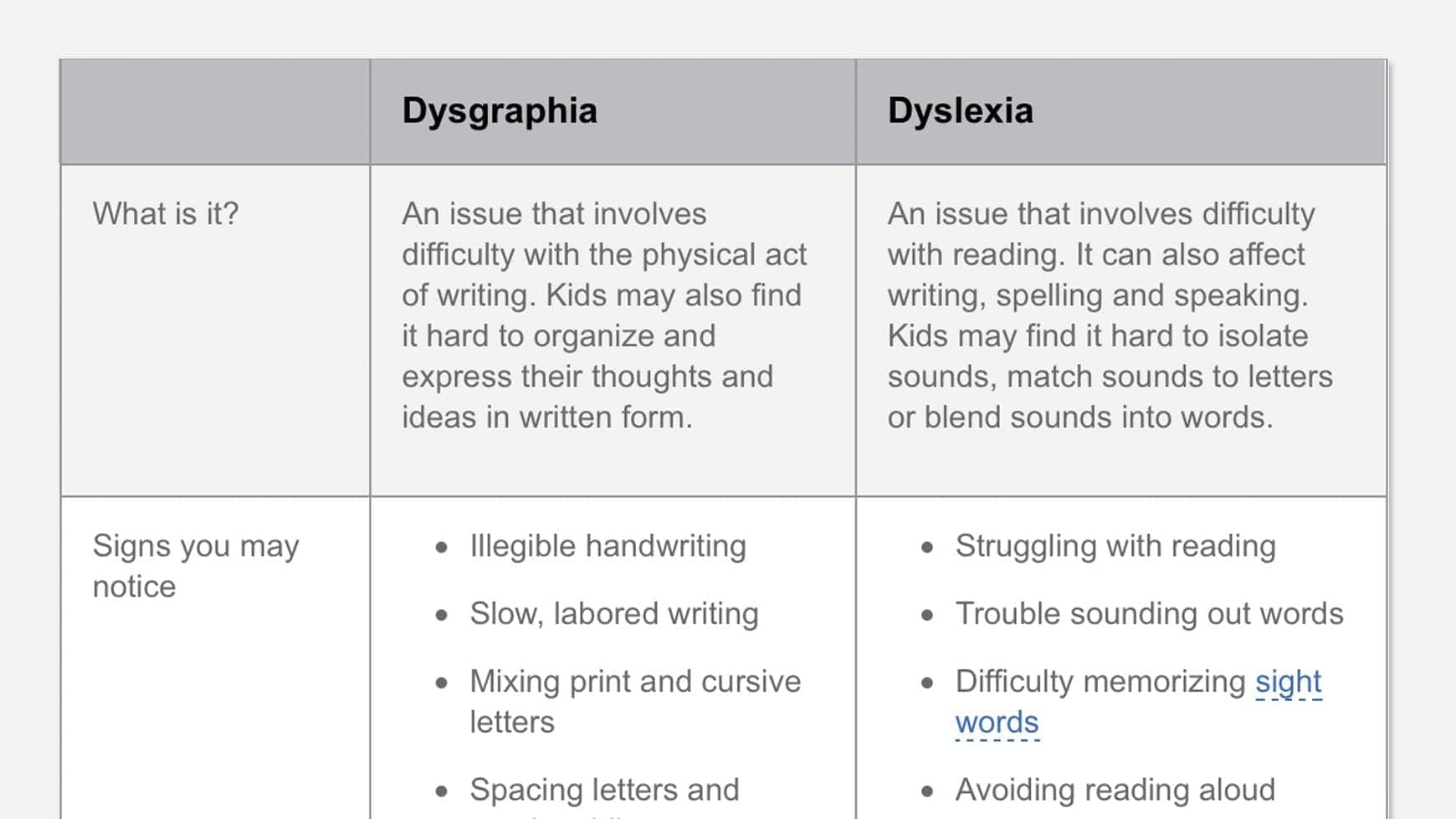
- Learning disabilities
- dysgraphia
- dyslexia
- Creativity
- ability to generate, create or discover new ideas, solutions and possibilities
- divergent thinking-“outside of the box”
- facet of intelligence-difficult to measure objectively
6.2 Language
- Use of words and systematic rules to transmit information (and solve problems)
- Form of communication used uniquely by humans
- Way of getting ideas from one person to another
- Spoken, written or signed
- Components of Language
- lexicon and grammar
- phoneme and morphemes combined to form word
- syntax and semantics used to construct language
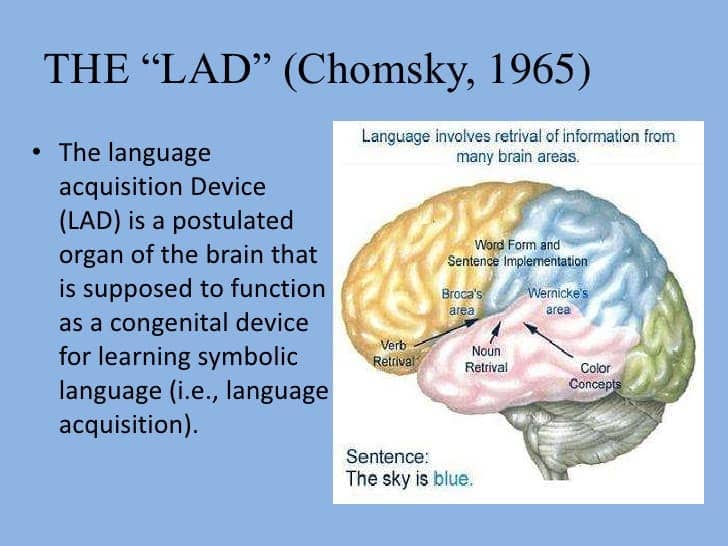
- Noam Chomsky
- Language Acquisition Device
- Universal Built-in System
6.3 Memory
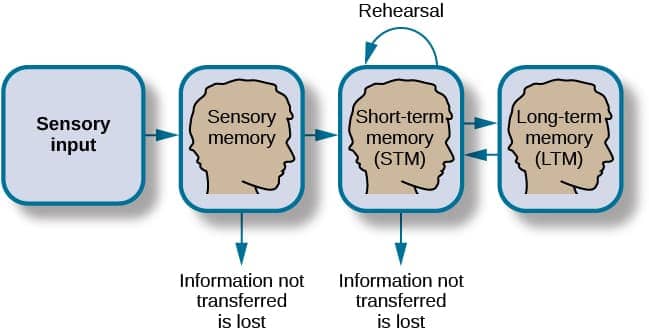
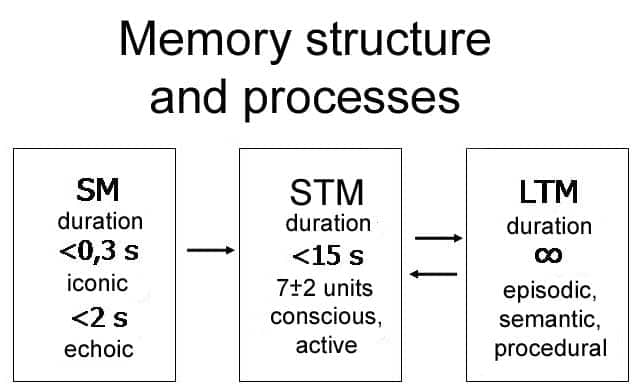
- Sensory memory
- the memory system that is triggered by the various senses that we have
- lasts only brief moments, seconds and nanoseconds
- Short-term/working memory
- information left in the mind long enough to solve problems
- Capacity of 7 items +/- 2
- Long-term memory
- extra effort required to transfer from short-term
- Unlimited capacity
- Mnemonic strategies
- can be deliberate or unconscious
- method of getting information into long-term memory or keeping more in short-term
- rehearsal, chunking, spelling
6.4 Thinking and Problem Solving
Heuristics
representativeness heuristic

availability heuristic

Trial and Error
Algorithm
Problem solving pitfalls (Biases)
- confirmation
- hindsight
- representative
- availability

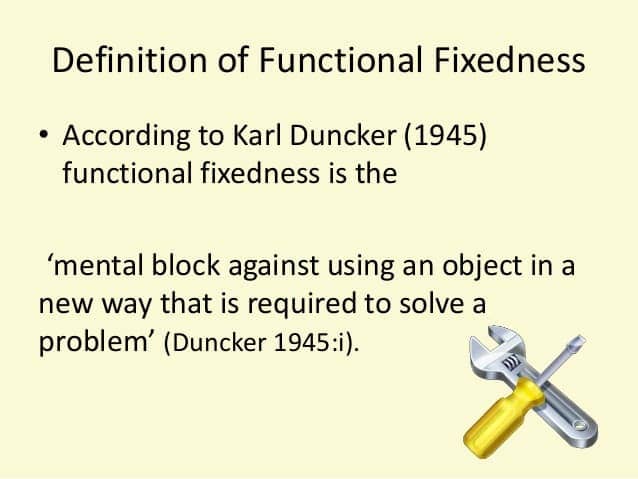
Functional fixedness
- become very limited in seeing the utility of things in my environment.
Quiz
- Priming is considered part of implicit memory because it
- (A) occurs without conscious awareness
- (B) often involves emotions
- (C) helps in recognition but not in recall
- (D) plays an important role in autobiographical memory
- (E) requires deep encoding
- In problem solving, which of the following approaches almost always guarantees a correct solution?
- (A) Insight
- (B) Heuristic
- (C) Algorithm
- (D) Critical thinking
- (E) Convergent thinking